Blood Grouping in Humans, Uses, Disorders- Erythroblastosis fetalis
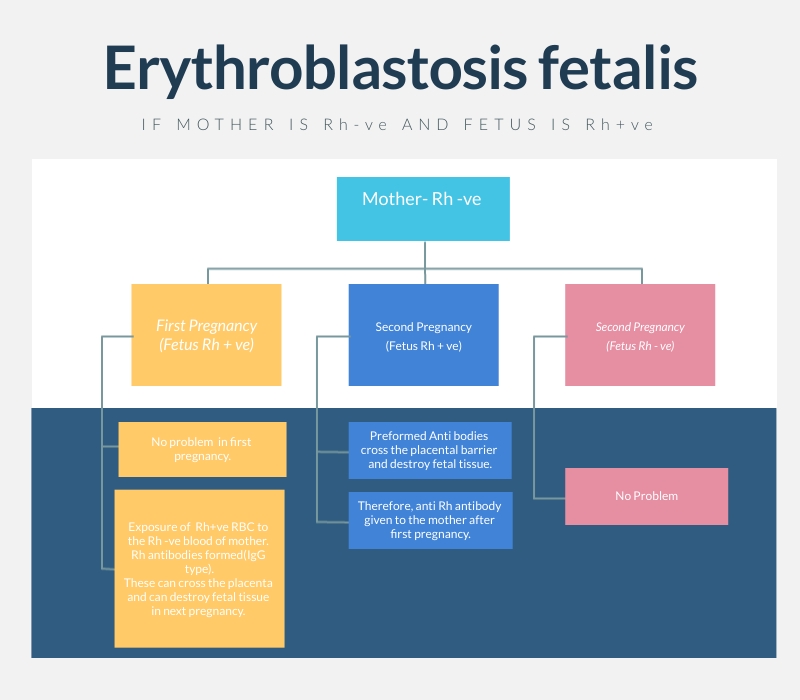
What do we mean by blood grouping? The surface of RBC contains certain antigens. It is these antigens on the basis of which the blood groups are decided. Different types of Blood Grouping ABO blood grouping- chromosome 9 (it has four different types of blood groups- A,B,AB,O) (AB blood group is a very good example of Co-dominance). Rh Antigen-If Rh antigen present then it is Rh +ve , and if absent then it is Rh -ve MN blood grouping- chromosome 4 Duffy antigen- chromosome 1, first blood system antigen to be localized. Bombay blood group-Chromosome 19. Another antigen present on the RBC is the H antigen. H antigen is necessary for the expression of A,B antigens on the RBC surface. O blood group has got only the H antigen. Now if this antigen is also absent the surface RBC then it is known as the Bombay blood group. Landsteiner's Law I - If an antigen is present on the RBC corresponding antibody must be absent in the plasma. eg- A person with A blood...


